Global IT supply chain
International transportation + IT O&M outsourcing + self-owned backbone network
In recent years, an increasing number of businesses involved in overseas operations—such as TikTok marketing and international e-commerce—have encountered the challenges of managing native IPs and broadcast IPs. This comprehensive guide explains how to query native IPs and broadcast IPs, enabling you to mitigate operational risks and ensure seamless international connectivity.

I. Core Concepts of IP Types
What is a Native IP?
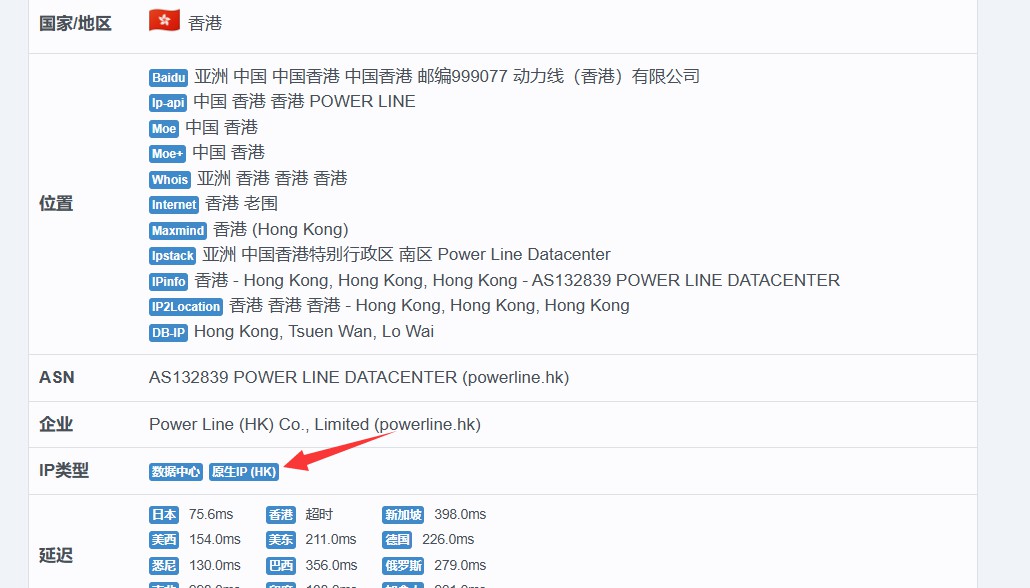
Native IP (also known as Local IP) is a technical concept widely accepted in the industry. Its determination primarily relies on the consistency between the IP’s registered location and its actual usage location. For example, if an IP registered in Hong Kong is routed through the United States and then used back in Hong Kong, it qualifies as a native IP in that locale.
Key Benefits:
Geographic Stability: Native IPs are ideal for long-term operations due to their consistent geographic association.
Operational Reliability: For multinational e-commerce platforms and social media account management, native IPs provide a stable and reliable network environment.
What is a Broadcast IP?
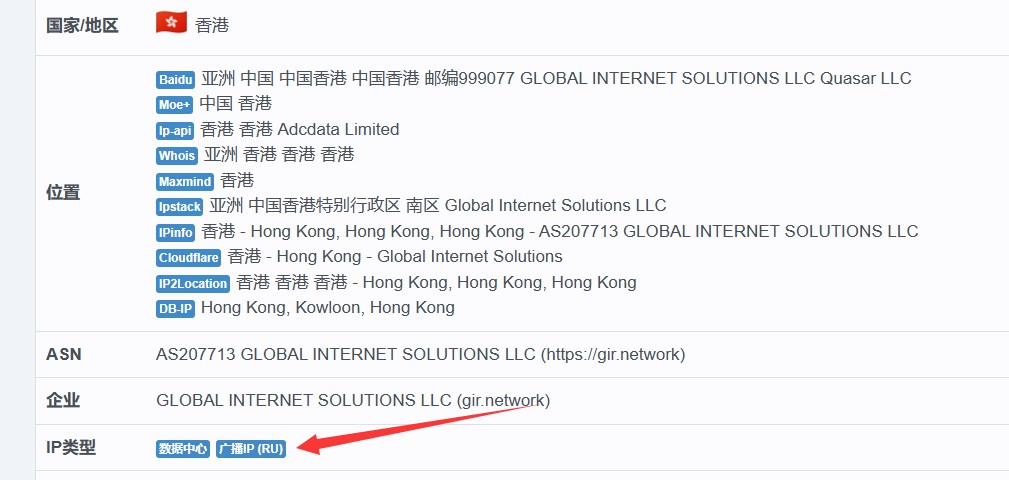
Broadcast IPs leverage the BGP routing protocol to facilitate cross-regional deployment, effectively separating the IP’s registration location from the server’s physical location. This is achieved when cloud service providers authorize their own IP address ranges to be used in overseas data centers, enabling the global scheduling of IP resources.
Key Benefits and Considerations:
Cost Advantages: Broadcast IPs can be more cost-effective, as IP resources can be dynamically allocated across regions.
Risk Factors: Despite their economic benefits, some online platforms may detect the attribute differences of broadcast IPs, which can lead to account irregularities or security concerns.
II. Methods for Distinguishing Between Native and Broadcast IPs
Dual-Dimensional Verification System
To accurately identify the type of IP, it is essential to verify two critical elements simultaneously:
IP Registration Records: Confirming the official registration information.
Real-Time Geographic Location: Checking the current physical location of the IP.
It is highly recommended to use professional tools, such as IPlark, to perform this dual verification and ensure accurate results.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using the IPlark Tool
Log in to the IPlark Website: Access the official IPlark platform.
Input the Target IP: Enter the IP address you wish to verify in the query window.
Generate a Visual Report: The system will automatically create a detailed report that includes:
IP registration agency records
Current physical location data
ASN (Autonomous System Number)
Network service provider details
Interpretation of Results:
Native IP: The report will show a complete match between the registered location and the current usage location.
Broadcast IP: The report will reveal cross-border deployment characteristics, indicating a separation between the registration and usage locations.
Native IP
Broadcast IP
III. Recommended Industry Solutions
For enterprise users seeking compliant and secure IP resources, partnering with professional service providers like Ogcloud is advisable. Ogcloud offers a range of advanced services, including: Overseas Cloud Phones with Pure IP, International Private Leased Lines, SD-WAN Solutions and other network solutions.
These solutions have undergone rigorous technical validations by mainstream platforms such as Amazon and TikTok, ensuring that they meet the highest standards for account security and network stability. Enterprises can select solutions based on their specific business scales and operational needs, with the added benefit of free trial consultations available through Ogcloud.

International transportation + IT O&M outsourcing + self-owned backbone network

Cellular chips + overseas GPS + global acceleration network

Overseas server room nodes + dedicated lines + global acceleration network

Global acceleration network + self-developed patented technology + easy linking

Global Acceleration Network + Global Multi-Node + Cloud Network Integration


